The Sacred Island of Okinoshima and Associated Sites in the Munakata Region is a UNESCO World Heritage site located in Japan. The site comprises three locations in the Munakata region of Fukuoka Prefecture: Okinoshima Island, Munakata Taisha Shrine, and associated archaeological sites on the nearby mainland.
Okinoshima Island is a sacred island that has been considered a sacred place for worship and pilgrimage for over a thousand years. The island is only accessible to a limited number of visitors each year, and strict rules govern what can be taken on the island and how visitors should behave.
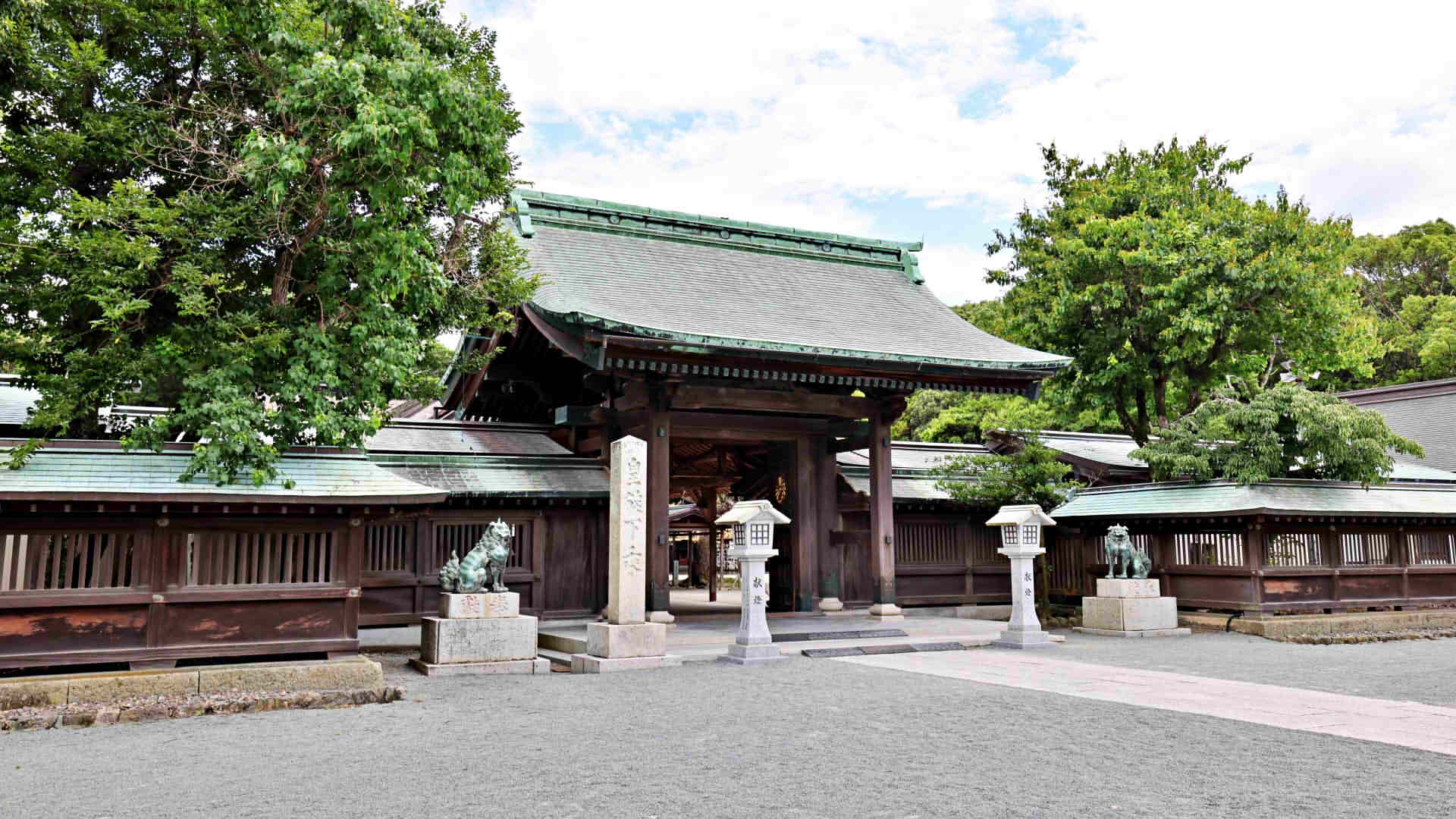
Munakata Taisha Shrine is a Shinto shrine located on the nearby mainland that has been an important center of worship for over 1,300 years. The shrine is dedicated to the three female deities of Munakata, who are believed to protect sailors and seafarers.
The associated archaeological sites include a number of important historical and cultural sites related to the worship of the Munakata deities, including burial mounds, ritual sites, and other archaeological remains.
The Sacred Island of Okinoshima and Associated Sites in the Munakata Region is significant not only for its religious and cultural value but also for its role in the development of early maritime trade and exchange in the region. The island was an important center of trade and exchange between Japan and neighboring countries, and artifacts found on the island have provided important insights into early maritime trade networks in the region.
In 2017, the Sacred Island of Okinoshima and Associated Sites in the Munakata Region was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage list as a cultural property, recognizing its importance as a cultural and historical landmark and its contribution to the understanding of the history of religion and trade in Japan.
Related Articles